Category: Ships
-
Japanese Battleship Iwami
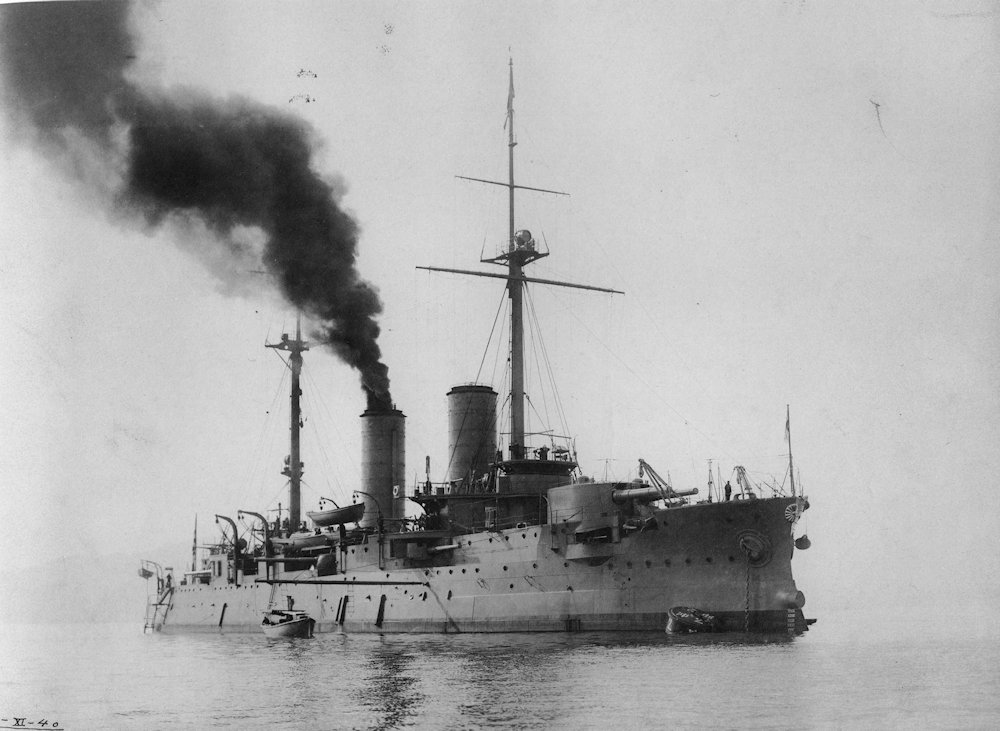
Japanese Battleship Iwami Iwami was a Borodino-class pre-dreadnought battleship captured by Japan after the Battle of Tsushima on 27 May 1905. Renamed Iwami, she was rebuilt between 1905 and 1907 and she was commissioned into the Imperial Japanese Navy on 2 November 1907. At the start of the Japanese intervention in Siberia during the Russian… Read more
-
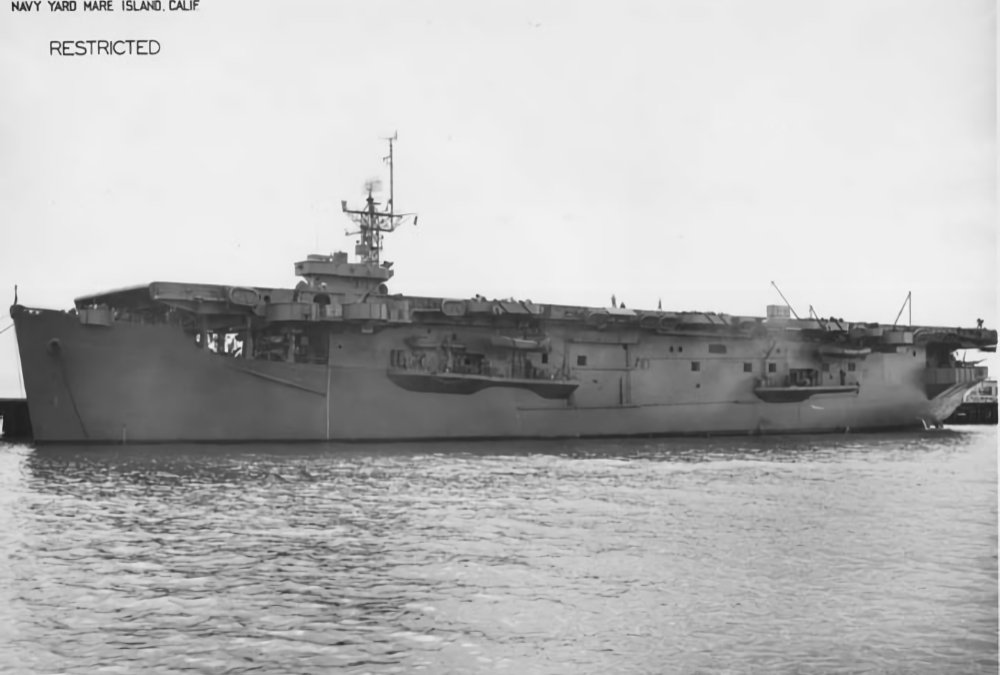
US Escort Carrier USS Altamaha CVE-18
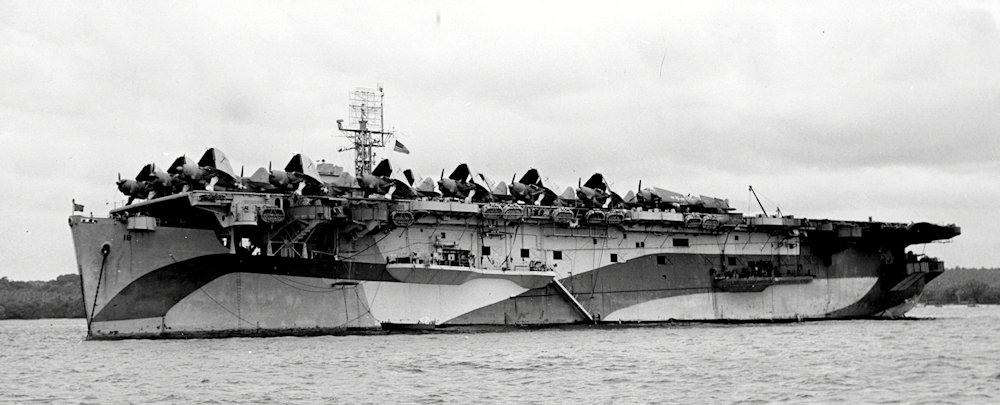

US Escort Carrier USS Altamaha CVE-18 Launched on 22 May 1942 and commissioned on 15 September 1942, USS Altamaha (AVG-18/ACV-18/CVE-18) was a Bogue-class escort aircraft carrier in the United States Navy during World War II. Before commissioning, her designation was changed from AGV-18 to ACV-18. On 15 July 1943 the designation was changed again, this… Read more
