Tag: Military
-
Horten Ho 229
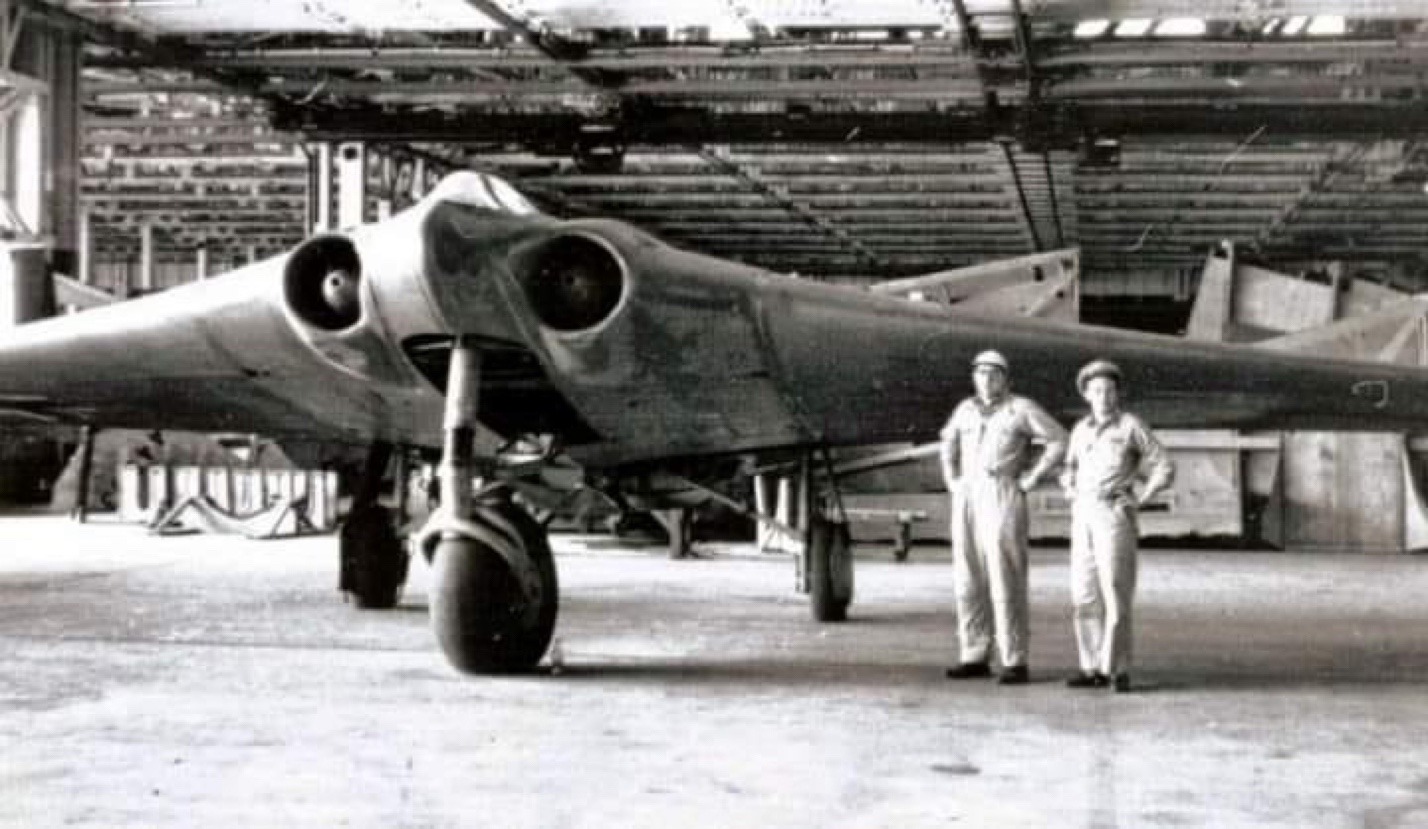
Horten Ho 229 The Horten Ho 229 was a German fighter-bomber flying wing developed during the Second World War. At one stage 100 had been ordered, although this was later reduced to 20 and none were delivered to the Luftwaffe. The first prototype, the Horten H.IX V1 was an unpowered glider first flew on 1… Read more
-
US Escort Carrier USS Nassau CVE-16
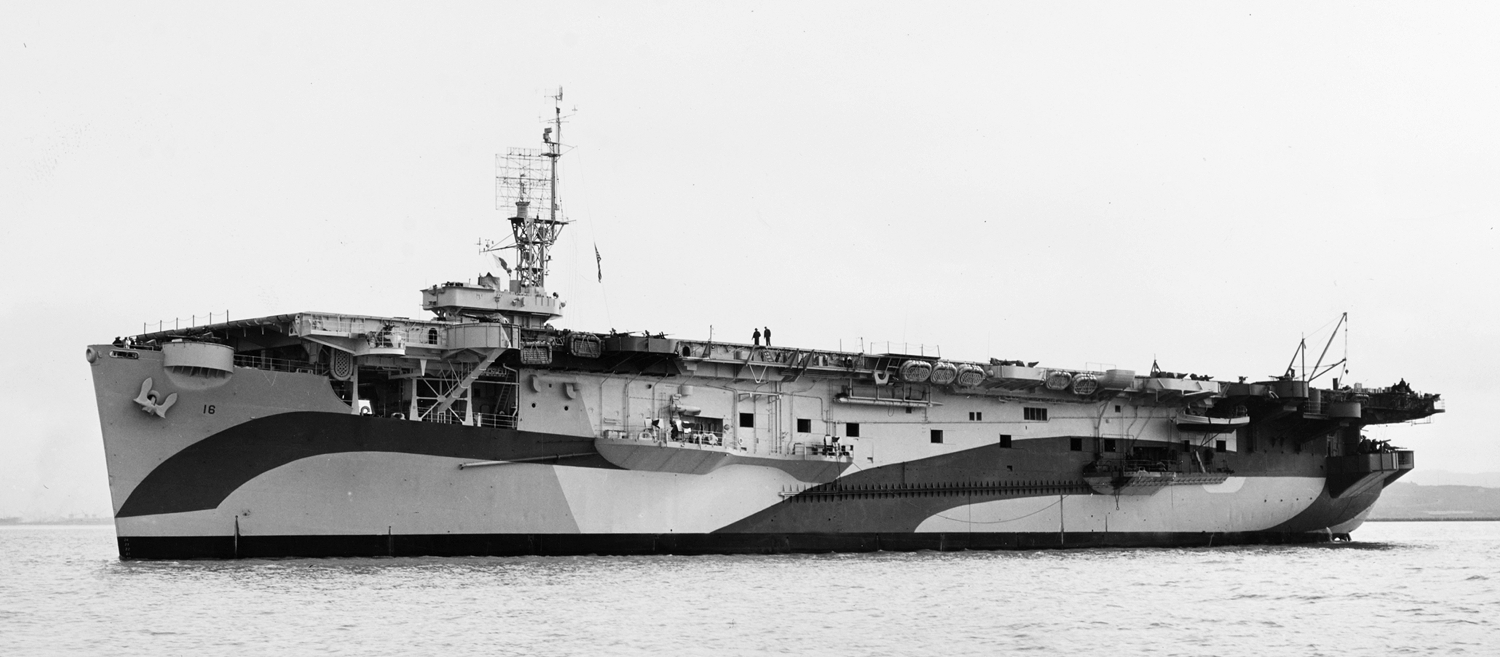

US Escort Carrier USS Nassau CVE-16 Originally classified as AVG-16, USS Nassau was reclassified as ACV-16 before her launch on 4 April 1942. Commissioned on 20 August 1942. Until April 1943 she operated as an aircraft transport in the Pacific. From 4 to 20 May 1943, she operated with Task Force 51, during which time… Read more
-
HMS Devastation (1871)
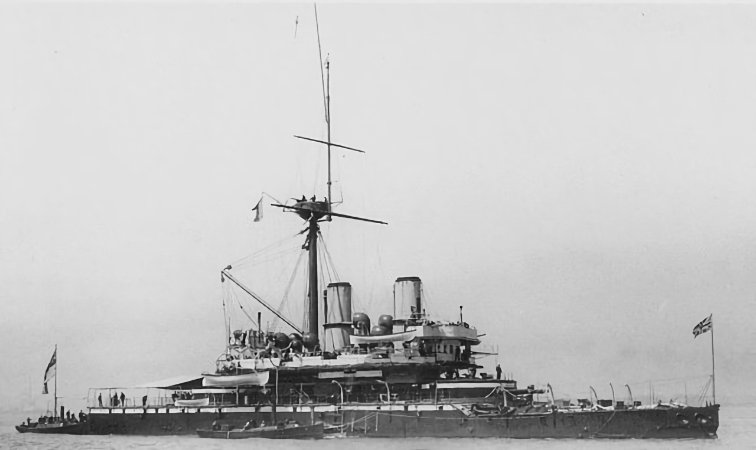
HMS Devastation (1871) HMS Devastation was the lead ship of her class of mastless ironclad turret ships built for the Royal Navy. Along with her sister HMS Thunderer (1872), she was the first class of ocean-going capital ships that did not carry sails, and the first in which the entire main armament was mounted on… Read more