Tag: Ship
-
Japanese Battleship Iwami
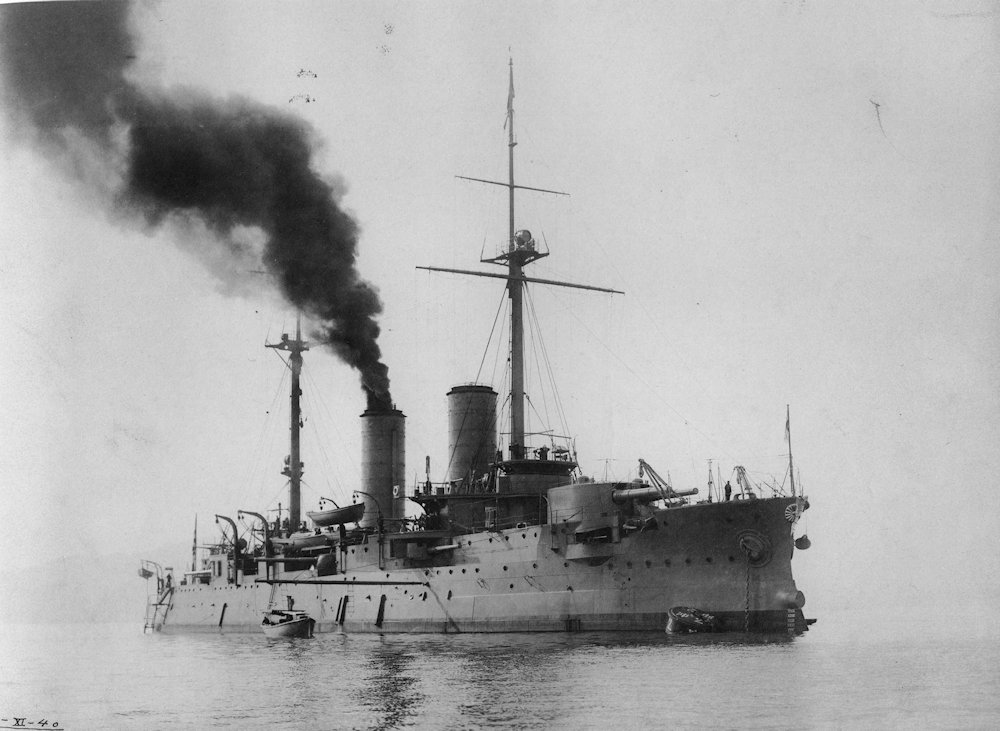
Japanese Battleship Iwami Iwami was a Borodino-class pre-dreadnought battleship captured by Japan after the Battle of Tsushima on 27 May 1905. Renamed Iwami, she was rebuilt between 1905 and 1907 and she was commissioned into the Imperial Japanese Navy on 2 November 1907. At the start of the Japanese intervention in Siberia during the Russian… Read more
-
Russian Battleship Orel
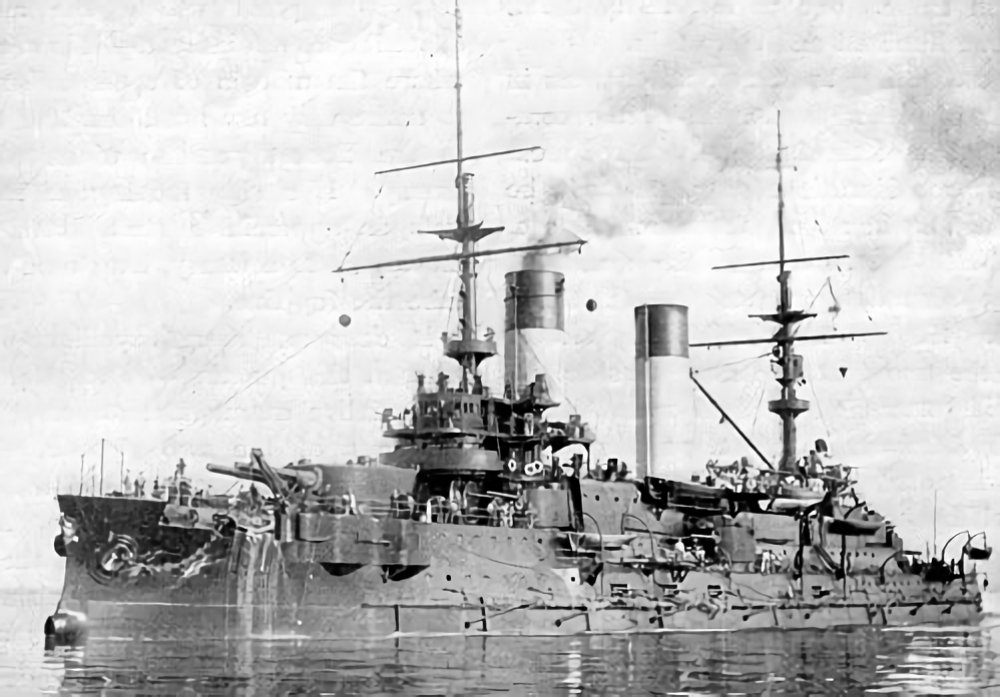
Russian Battleship Orel Launched on 19 July 1902, Orel (sometimes Oryol) was a Borodino-class pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Imperial Russian Navy. Entering service in October 1904, she sailed on 15 October 1904, with the Second Pacific Squadron to break the Japanese blockade of Port Arthur. The Japanese captured the port while the squadron was in… Read more
-
Russian Battleship Imperator Aleksandr III
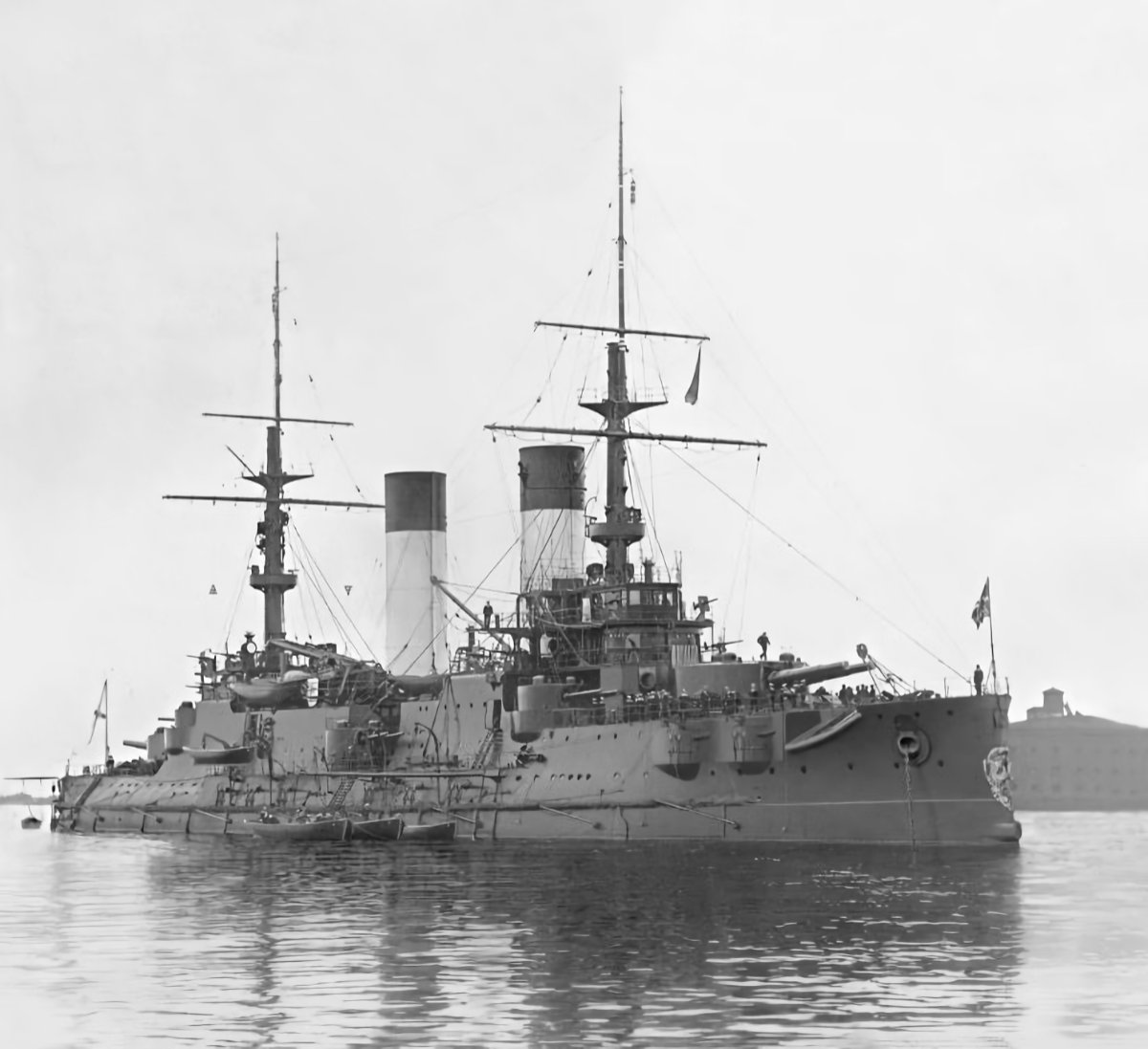

Russian Battleship Imperator Aleksandr III Launched on 3 August 1901, Imperator Aleksandr III was a Borodino-class pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Imperial Russian Navy. Entering service in November 1903, she sailed on 15 October 1904, with the Second Pacific Squadron to break the Japanese blockade of Port Arthur. The Japanese captured the port while the squadron… Read more