Tag: warship
-
Italian Battleship Giulio Cesare
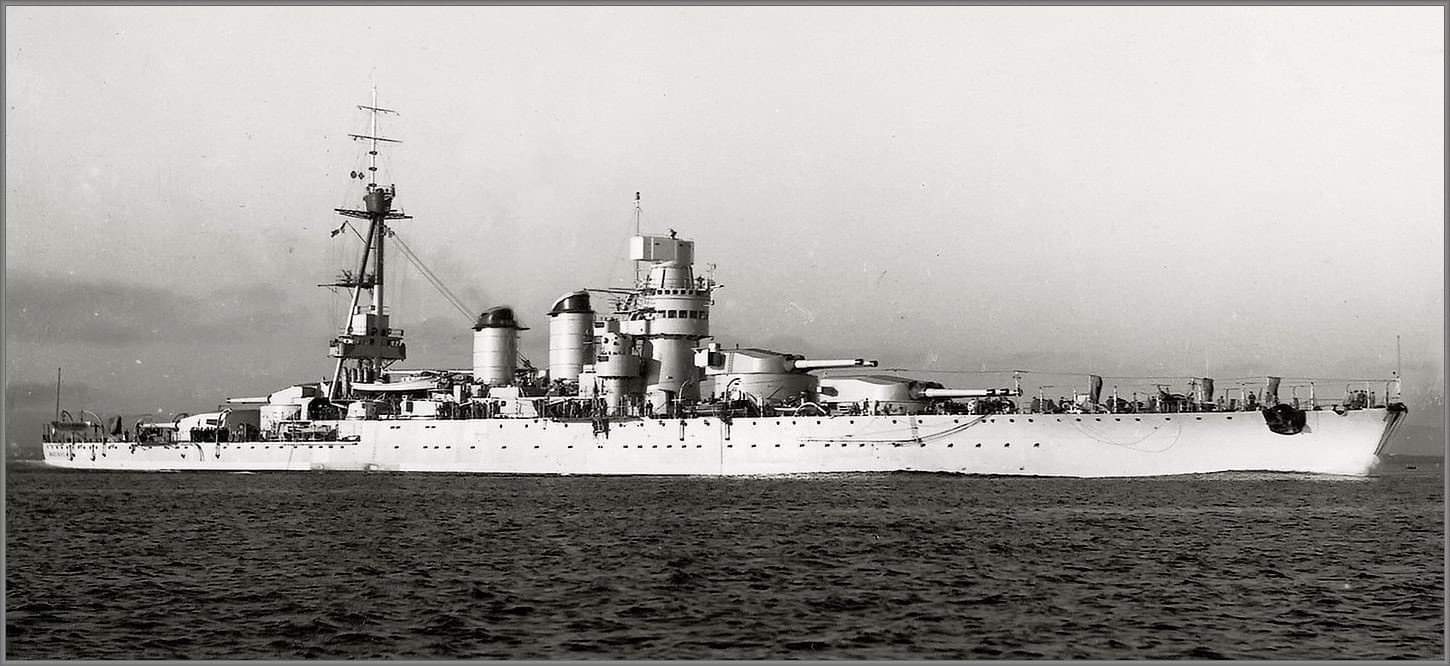

Italian Battleship Giulio Cesare Completed on 14 May 1914, Giulio Cesare was a Conte di Cavour-class dreadnought battleships built for the Regia Marina (Royal Italian Navy). She saw little service during the First World War, spending most of her time in port, ready to sortie if the Austro-Hungarian battlefleet sought a decisive engagement. During the… Read more
-
Soviet Battleship Novorossiysk
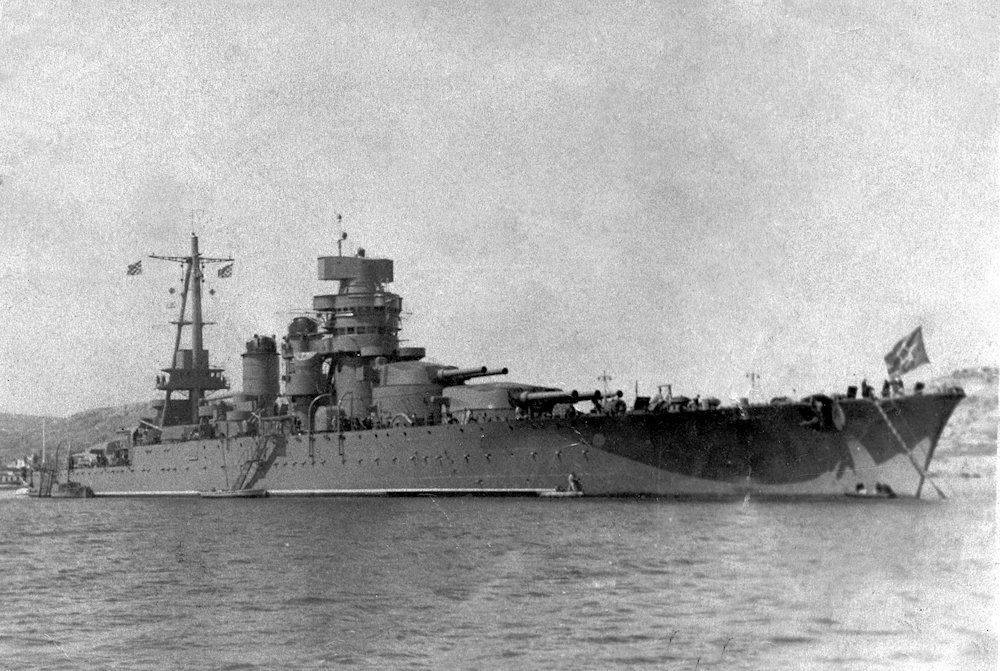
Soviet Battleship Novorossiysk Novorossiysk was a Conte di Cavour-class battleship operated by the Soviet Union from 1949 to 1955. Originally the Regia Marina (Italian Royal Navy) battleship Giulio Cesare, she was awarded to Russia as part of war reparations. Operated mainly as a training ship, she underwent several refits, which included replacing her lights Italian… Read more
-
Russian Battleship Imperatritsa Mariya
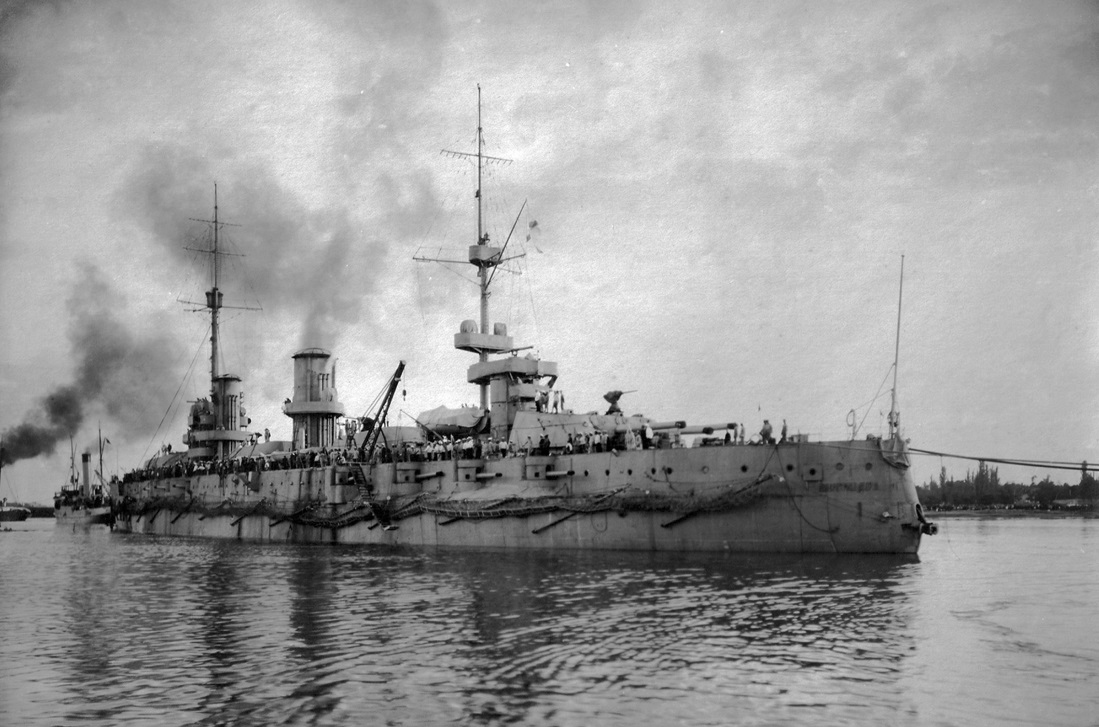

Russian Battleship Imperatritsa Mariya Imperatritsa Mariya was the lead ship of her class of battleships built for the Imperial Russian navy, along with her sister ships Imperatritsa Ekaterina Velikaya and Imperator Aleksandr III. Launched on 19 October 1913, she was completed on 10 June 1915. During the First World War, she supported older battleships when… Read more