Tag: warship
-
Danish Coastal Defense Ship HDMS Herluf Trolle (1899)
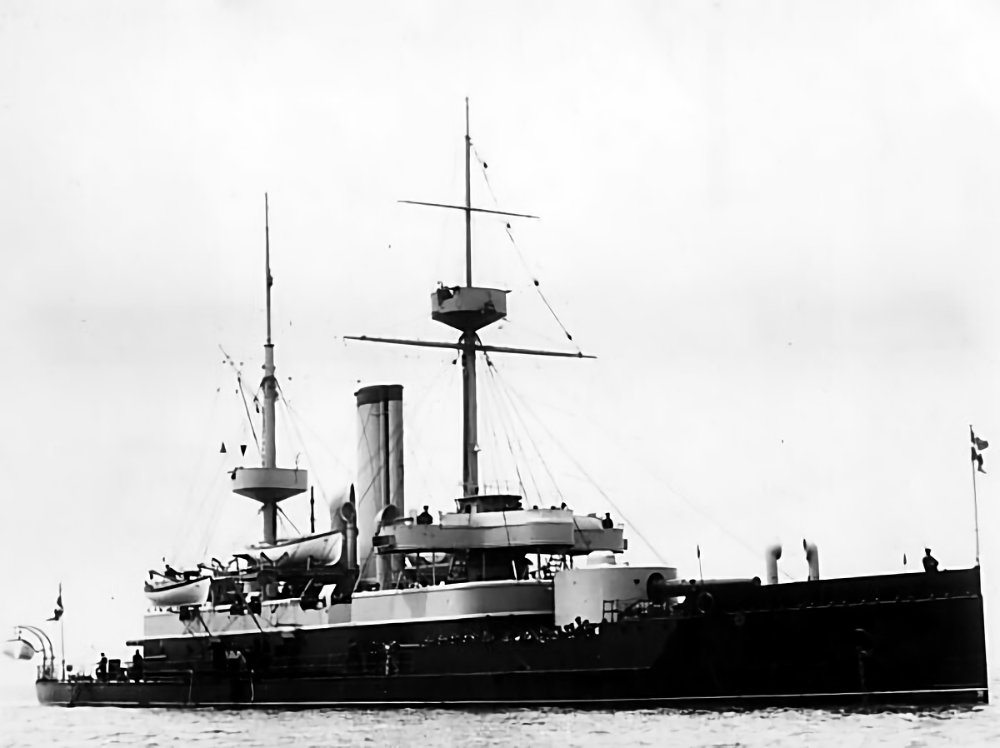

Danish Coastal Defense Ship HDMS Herluf Trolle (1899) HDMS Herluf Trolle (1899) was a Danish coastal defense ship. The first of her class of three ships (including Olfert Fischer and Peder Skram), she was launched on 2 September 1899 and commissioned on 7 June 1901. She had an uneventful career, as Denmark remained neutral throughout World War One. Herluf… Read more
-
Russian Battleship Imperatritsa Ekaterina Velikaya
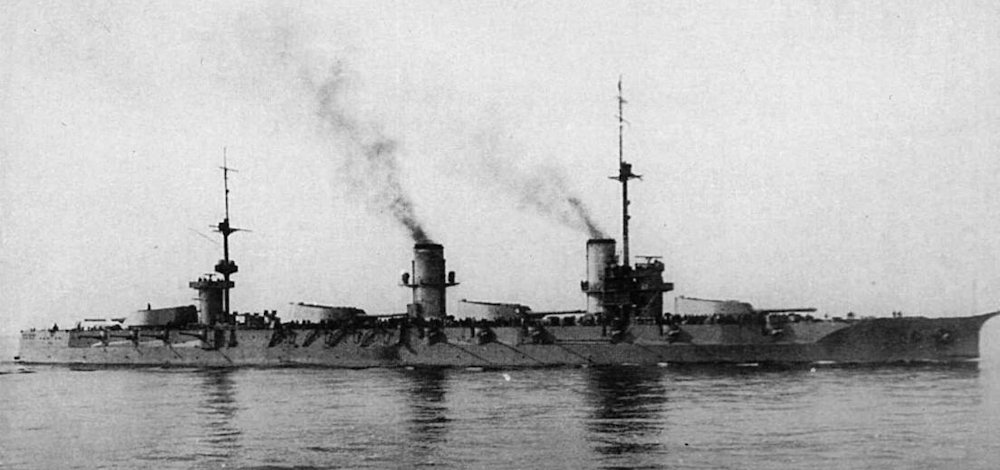
Russian Battleship Imperatritsa Ekaterina Velikaya Commissioned on 18 October 1915, Imperatritsa Ekaterina Velikaya, was the second of the three Imperatritsa Mariya-class dreadnoughts built for the Imperial Russian Navy. Her two sister were Imperatritsa Mariya and Imperator Aleksandr III. During the First World War, she engaged the Turkish battlecruiser Yavûz Sultân Selîm (ex-German Goeben) once, but… Read more
-
Russian Battleship Imperator Aleksandr III
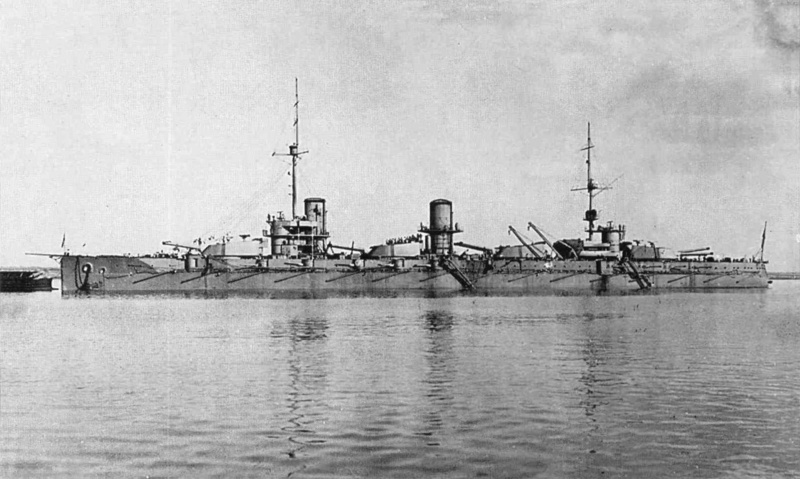
Russian Battleship Imperator Aleksandr III Imperator Aleksandr III was a battleship built for the Imperial Russian Navy. The third and last of the three ship Imperatritsa Mariya-class (along with her sisters Imperatritsa Ekaterina Velikaya and Imperatritsa Mariya), she was launched 15 April 1914. Completion was delayed as effort was concentrated on her two more advanced… Read more