Tag: World War Two
-
Canadian Aircraft Carrier HMCS Warrior
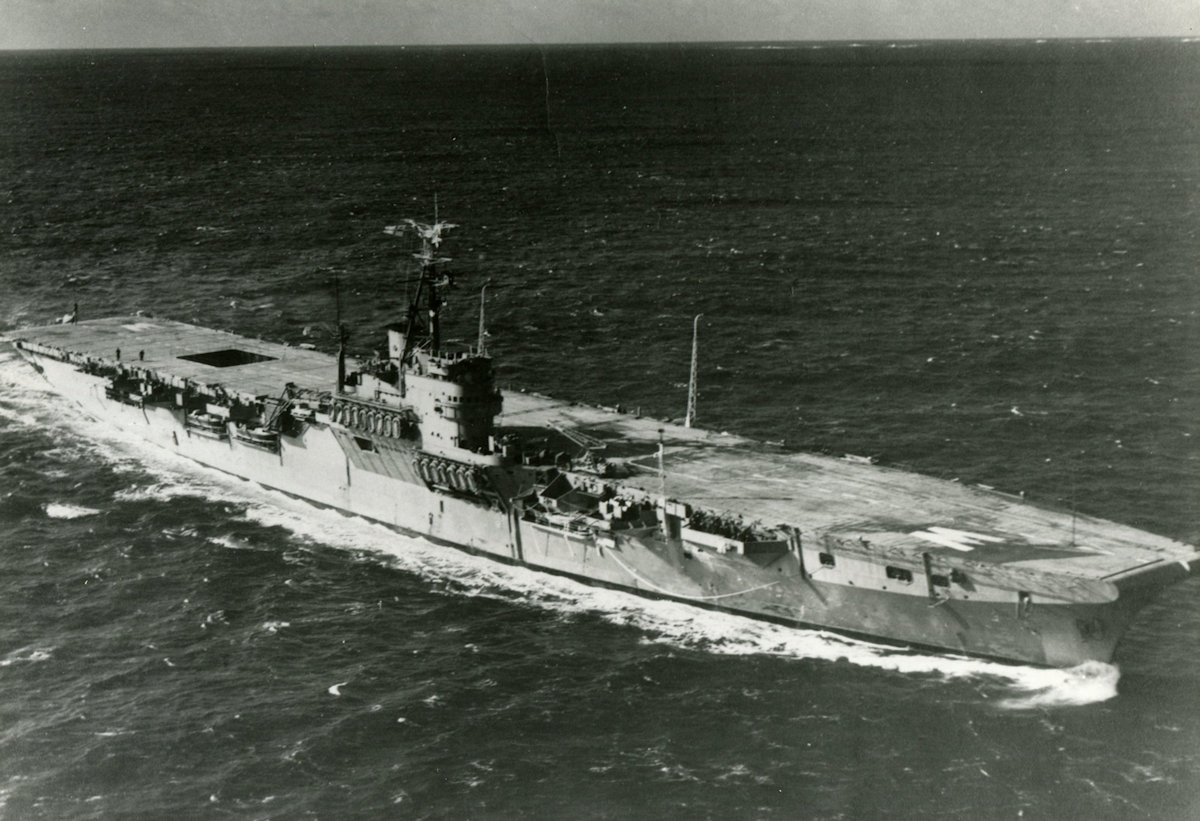
Canadian Aircraft Carrier HMCS Warrior Laid down on 12 December 1942 as HMS Warrior, a Colossus-class light-aircraft carrier for the Royal Navy, the ship was loaned to the Royal Canadian Navy as HMCS Warrior. Commissioned on 24 January 1946, she lacked heating for some of the onboard equipment, as the Royal Navy had intended her… Read more
-
Republic XF-12 Rainbow
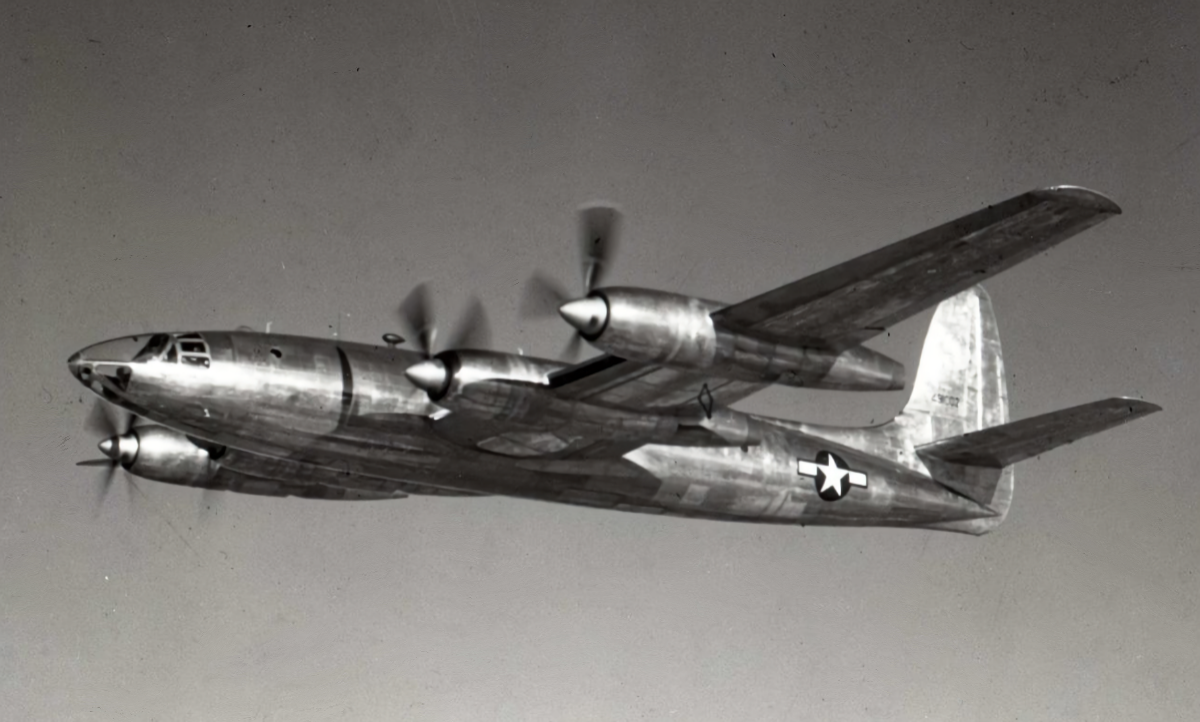

Republic XF-12 Rainbow The Republic XF-12 Rainbow was a four-engined reconnaissance aircraft designed for the USAAF. Designed during the Second World War, the first of two prototypes had its first flight on the 4th of February 1946. On the 10th of July 1947, the first prototype had its right main gear severed at the engine… Read more
-
US Aircraft Carrier USS Franklin CV-13
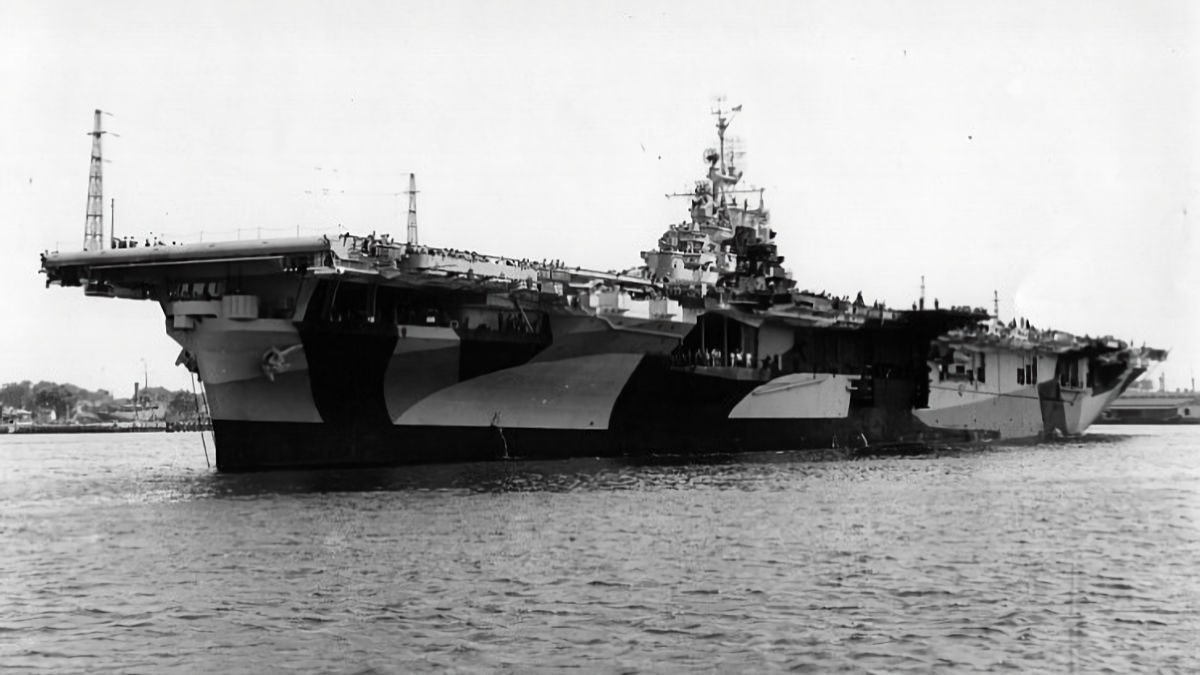

US Aircraft Carrier USS Franklin CV-13 Laid down on 7 December 1942 and launched on 14 October 1943, USS Franklin CV-13 was an Essex-class aircraft carrier of the US Navy. Commissioned into the navy on 31 January 1944 she then undertook a work-up phase before moving to the Pacific. From the end of June 1944,… Read more