Tag: World War Two
-
Bloch MB.170 French Reconnaissance Bomber
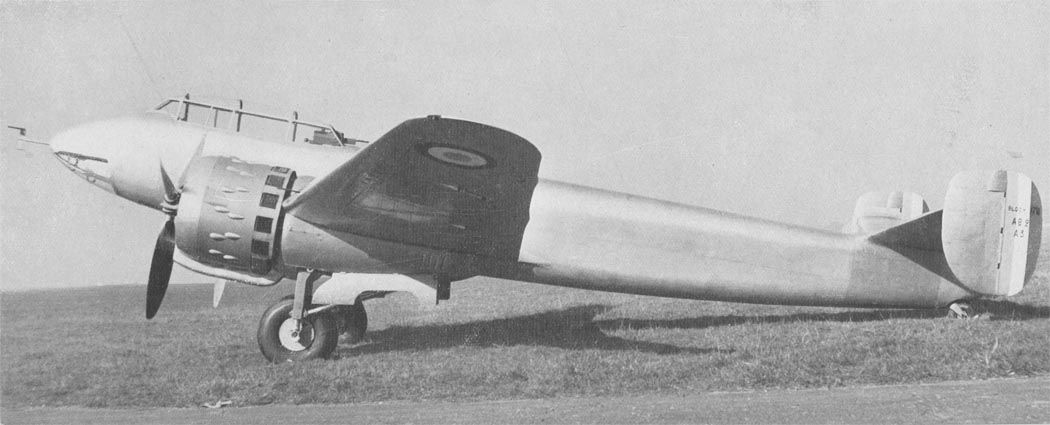
Bloch MB.170 French Reconnaissance Bomber Read more
-
Italian Battleship Giulio Cesare
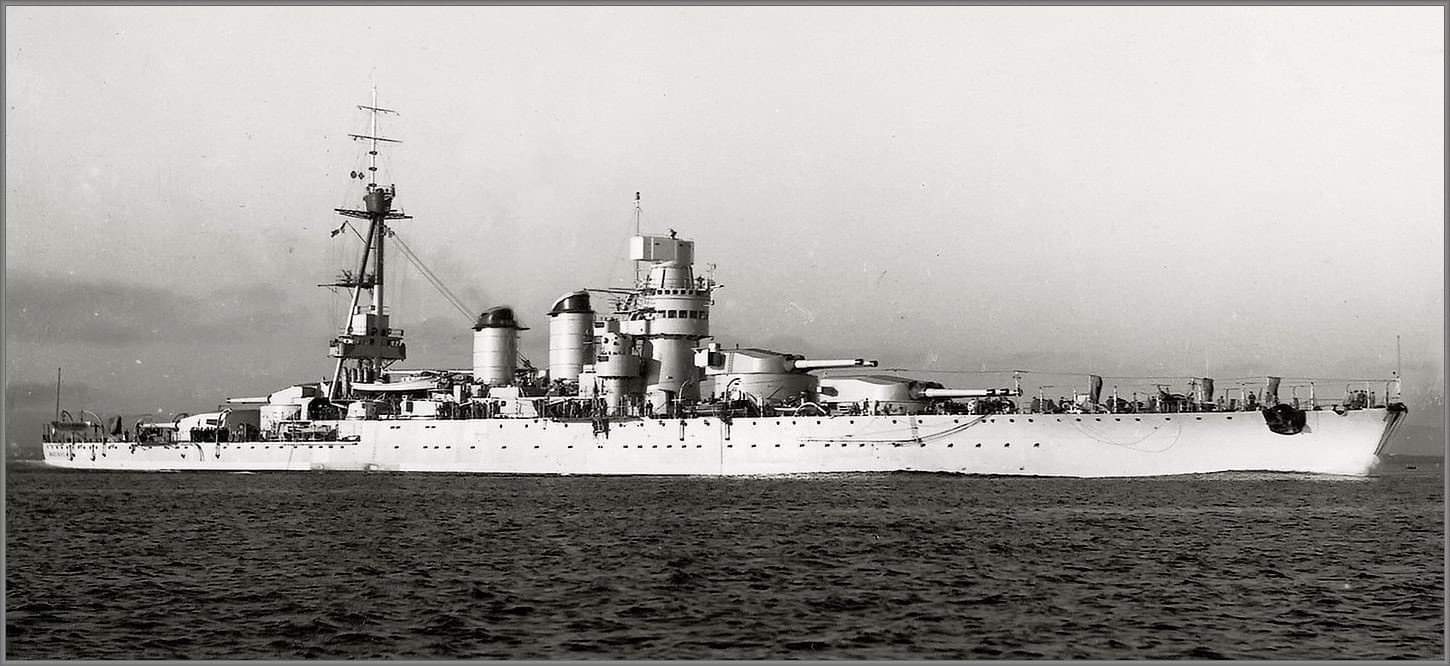

Italian Battleship Giulio Cesare Completed on 14 May 1914, Giulio Cesare was a Conte di Cavour-class dreadnought battleships built for the Regia Marina (Royal Italian Navy). She saw little service during the First World War, spending most of her time in port, ready to sortie if the Austro-Hungarian battlefleet sought a decisive engagement. During the… Read more
-
Finnish Submarine Saukko
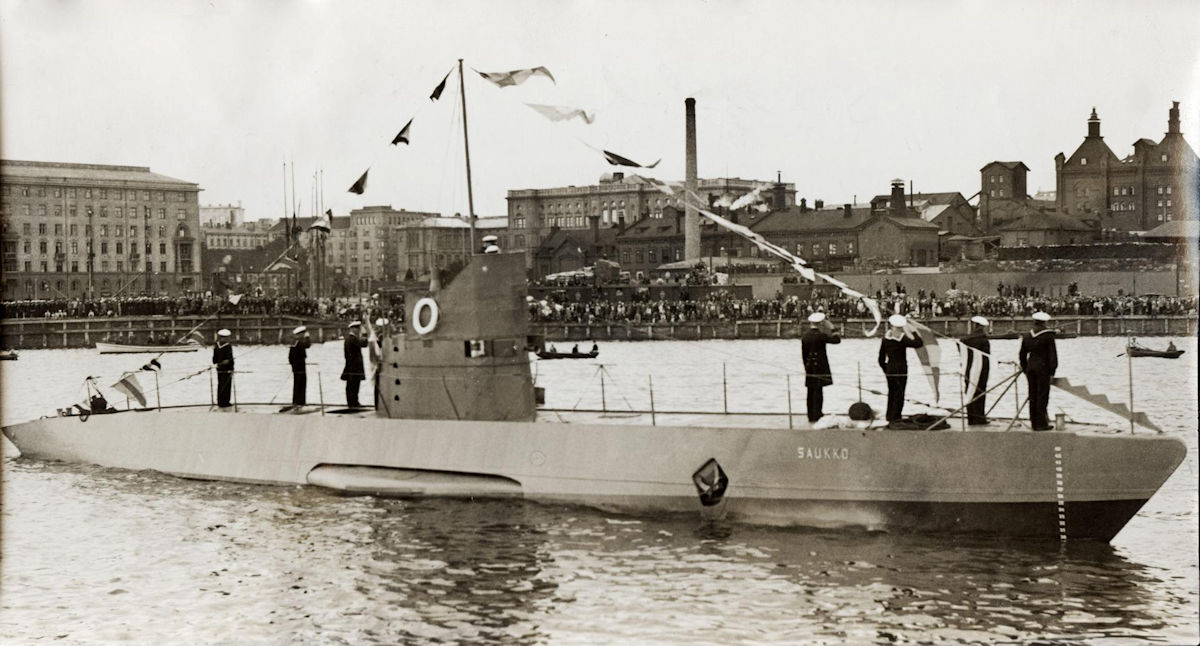
Finnish Submarine Saukko Saukko (Finnish for European otter) was a Finnish submarine launched in 1930. Designed to operated from Lake Ladoga, her tonnage was limited to 100 tonnes by the Treaty of Tartu. In reality, she weighted 114 tonnes and never operated from the lake. To enable rail transportation, she was able to be separated… Read more